Transport. Construction. Agriculture. Mining. Energy. Manufacturing. Military.
Whether it’s delivering food, moving raw materials, or helping to secure national interests, diesel engines keep the world turning.
Known for their durability, efficiency, and ability to handle any load they’re given, diesel engines are the workhorses of a wide range of essential industries. As such, the importance of proper “care and feeding” can’t be overstated. Diesel engines are investments and regular maintenance is crucial to get the best return from their performance. This comprehensive guide provides all the necessary information to keep your engine running its best, from a breakdown of components to how to perform routine checkups and even troubleshoot common operation issues.
Inside The Diesel Engine
Before considering maintenance procedures, it’s important to know and understand each of the pieces that make up a diesel engine:
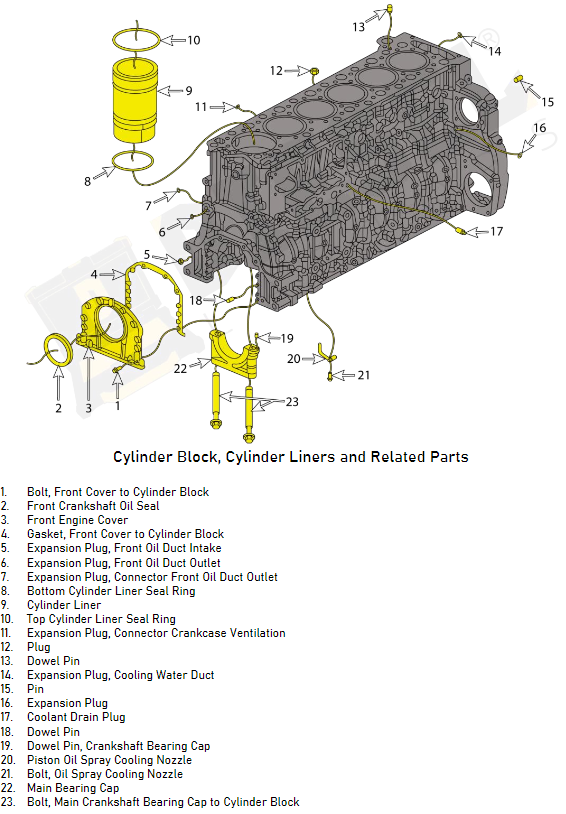
Cylinder Block
The cylinder block is the main structure of a diesel engine and houses the cylinders, the pistons, and the crankshaft. Usually cast out of iron or aluminum alloy, the cylinder block is designed to sustain the extreme pressure and temperature generated during combustion. The cylinder block should be regularly inspected for any cracks or wear and properly lubricated to keep all the moving parts inside functioning smoothly.
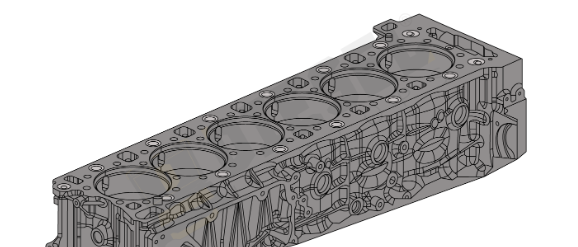
Cylinder Head
Seated on top of the cylinder block, the cylinder head seals the cylinders and houses the intake and valves that control the flow of air and exhaust gasses. Coolant and oil also pass through the cylinder head, providing temperature control and lubrication. Regular maintenance should include checking the cylinder head for warping or cracks, ensuring valve clearances are within specified ranges, and inspecting the condition of the fuel injectors to ensure proper operation inside the head.
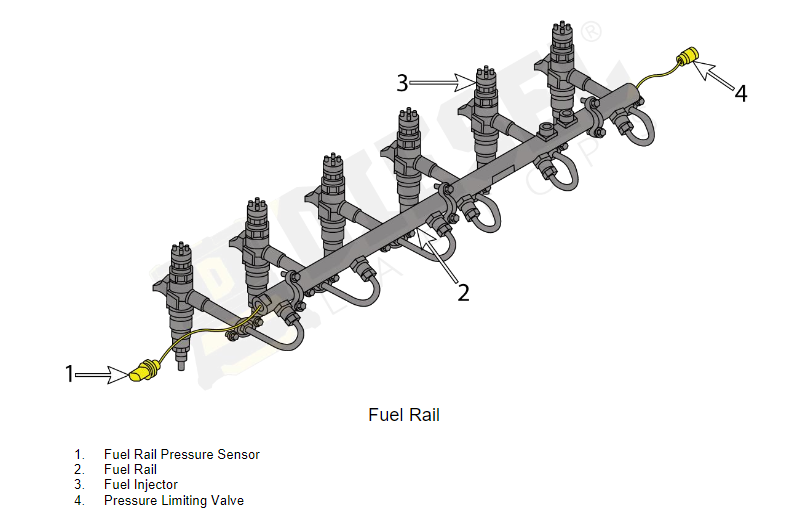
Fuel System
The fuel system stores, filters, and delivers fuel to the engine’s combustion chambers. Key components that form the fuel system include the fuel tank, fuel pump, fuel filters, and fuel injectors. Proper maintenance for the fuel system includes regularly replacing fuel filters, making sure the fuel pump is operating correctly, and cleaning or replacing injectors on a regular basis to prevent clogs.
Air Intake System
The air intake system is responsible for delivering clean air to the engine for the combustion process. The air intake system includes the air filter, the intake manifold, and a number of sensors. Individually, the air filter removes dirt, dust, and other impurities and the intake manifold distributes the purified air evenly to each cylinder. Routine maintenance of the air intake system should include inspecting and replacing the air filter, checking the intake manifold for leaks or blockages, and verifying all sensors are functioning properly for optimized air flow to the cylinders.
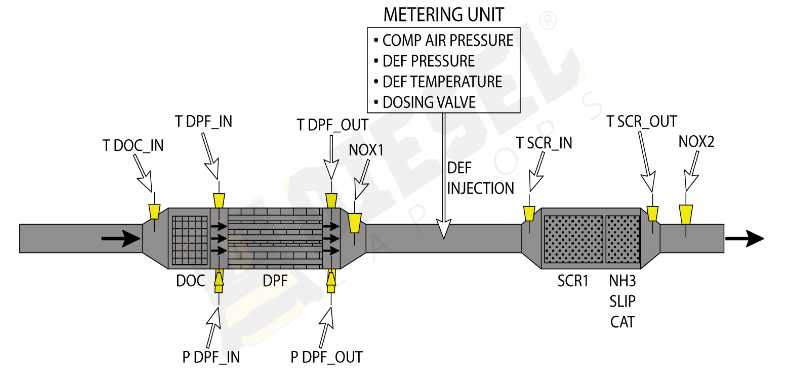
Exhaust System
The primary function of the exhaust system is to remove gasses from the engine after combustion, thereby reducing emissions and engine noise. The exhaust system includes the exhaust manifold, DPF and SCR systems, muffler, and tailpipe. Exhaust system maintenance includes regular inspection for leaks, corrosion, and damage, testing the DPF and SCR systems, inspecting the muffler, and replacing any worn-out parts to maintain efficient emission control and noise reduction.
Cooling System
With so much pressure and heat inside a diesel engine, the cooling system is vital. The cooling system is made up of the radiator, the water pump, the thermostat, and coolant hoses. To keep the cooling system operating efficiently and keep the engine within an optimal temperature range, coolant levels should be checked regularly, hoses and the radiator should be inspected for leaks or blockages, and the coolant and thermostat should be replaced as needed.
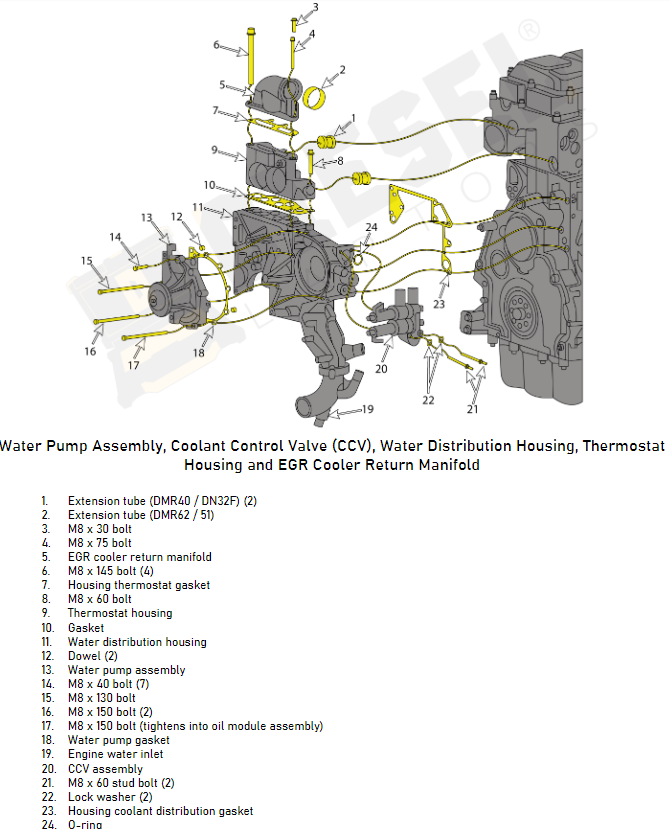
Lubrication System
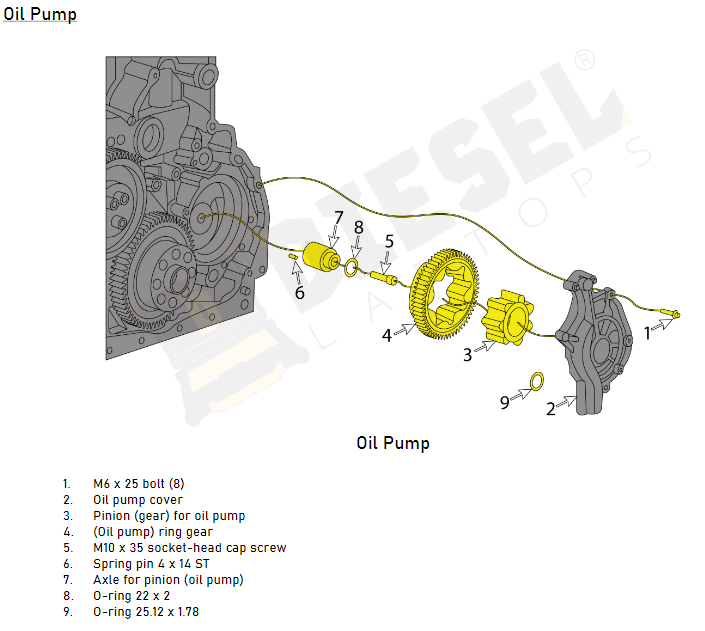
All of the moving parts within a diesel engine require lubrication to reduce friction and wear. The lubrication system includes the oil pump, oil filter, and various oil passages located throughout the engine. Lubrication is critical to prevent metal-on-metal contact, reduce heat build-up, and, overall, prolong the engine’s lifespan. Lubrication system maintenance includes checking oil levels, changing the oil and oil filter at regular intervals, and inspecting for leaks in the system to ensure it is operating as efficiently as possible.
Routine Maintenance
Though they can sometimes be a chore, routine maintenance checks are key to the longevity and efficiency of a diesel engine. Regular maintenance intervals and checkups can help identify potential issues before they become major problems, preventing expensive repairs and downtime.
This chart outlines essential maintenance tasks, from oil and filter changes to battery upkeep. By following these simple steps, you can maintain optimal performance, improve fuel efficiency, and extend the overall lifespan of your diesel engine.
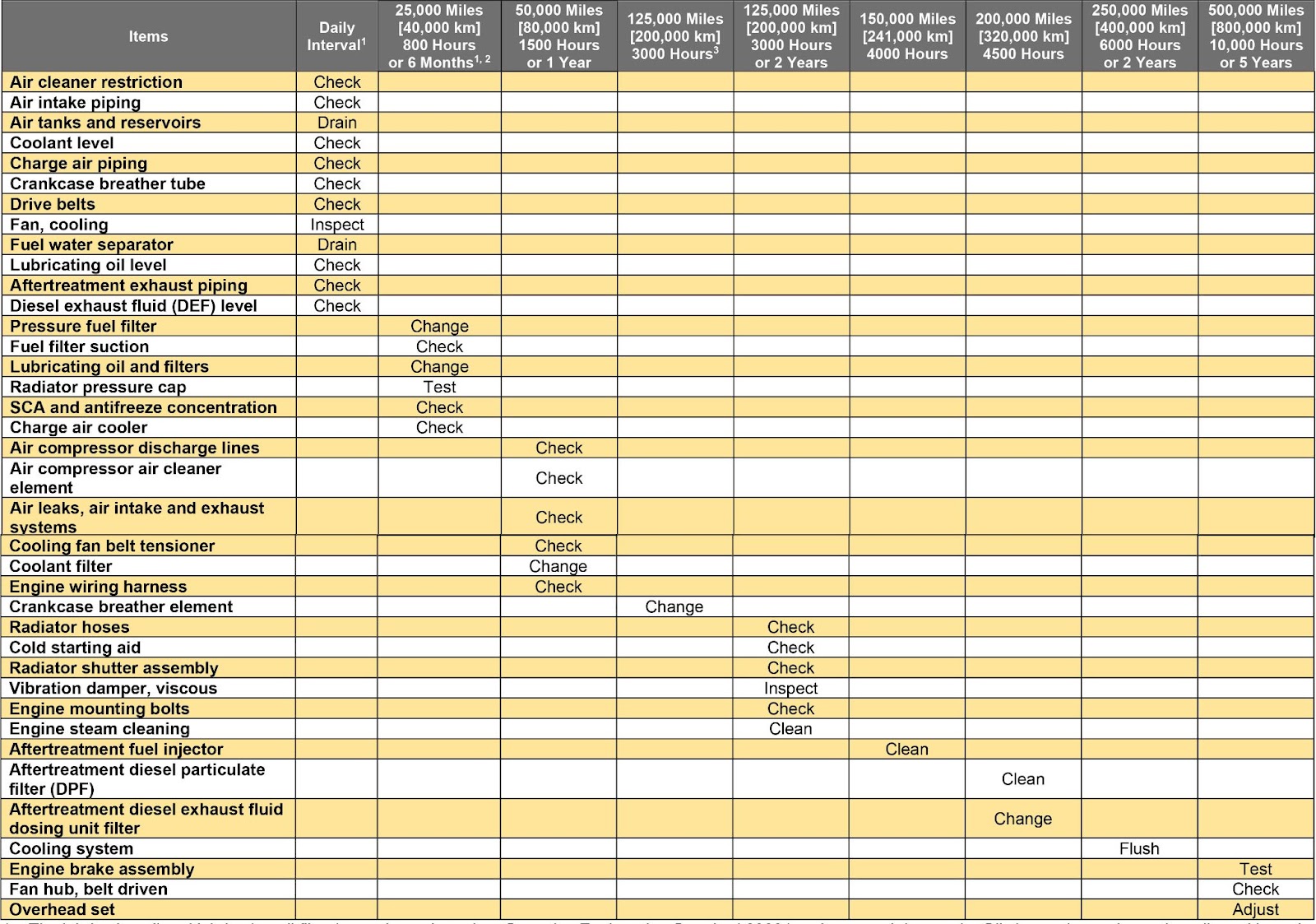
(Pictured above: Cummins ISX 11.9 CM2250 (2010-13) maintenance intervals, available in the Technical Repair Docs module on Diesel Repair)
It’s important to note that every engine has its own maintenance schedule, determined by variable factors such as engine operation hours, miles driven, and idle time.
The maintenance chart I’d clarify that every engine has different maintenance schedules and the schedules are different depending on variate of factors including engine hours, miles driven, and idle time. Make sure to specify which engine that is if you put the chart/images in there. IE, “Example of a 2012 Cummins ISX maintenance Schedule” or “Cylinder Head from 2016 Detroit Diesel Series 60”.
Oil and Filter Changes
Changing the oil and filter is generally recommended after about 25,000 miles, depending on manufacturer recommendations and operating conditions. Recent advances in engine efficiency and the quality of oil itself have increased the interval between oil changes significantly. Check your OEM’s recommendations.
Procedure:
- Step 1: Warm up the engine to ensure easy oil flow
- Step 2: Remove the drain plug and allow the oil oil to drain out completely
- Step 3: Replace the oil filter
- Step 4: Refill the oil with recommended type and quantity
Fuel System
Fuel Filter Replacement: Replace fuel filters regularly to prevent clogging and ensure clean fuel delivery.
Injector Cleaning: Use fuel additives or professional cleaning services to keep injectors clean and functioning properly
Not sure what filter you need? Diesel Laptops makes it easy with Find My Filter! Find My Filter cross-references exactly the part you need based on VIN, Year, Make, or Model and generates a comprehensive list of filters, categorized by manufacturer. Find My Filter streamlines your maintenance process and keeps your truck running smoothly with just one click.
Air Filter Replacement
Inspect and replace the air filter every 15,000 to 30,000 miles to ensure proper air flow and prevent contaminants from entering the engine block.
Cooling System
Coolant Level Check: Regularly check coolant level and top up as needed with recommended coolant type.
Radiator Inspection: Inspect the radiator for leaks and make sure there is no debris or buildup that could block airflow.
Battery
Terminal Cleaning: Keep battery terminals clean of corrosion.
Charge Check: Regularly check the battery’s charge and replace the battery if it shows signs of weakening.
Exhaust System Inspection
Visual Inspection: Check for signs of leaks, rust, or damage.
Emission Check: Ensure the engine meets all relevant emission standards.
Advanced Maintenance
Advanced maintenance procedures are geared towards complex issues that affect long-term reliability and performance of a diesel engine. Some of these tasks will require specialized knowledge and particular tools. However, understanding and performing these advanced maintenance procedures can have a significant impact on your diesel engine’s efficiency, power, and lifespan– and prevent catastrophic failures and severely expensive repairs.
- Valve Adjustment
- Check and adjust valve clearance as recommended by the OEM (usually around 200,000 miles with most commercial trucks).
- Remove the valve cover.
- Measure the clearance between the vale stem and the rocker arm.
- Adjust the clearance as needed to manufacturer specifications.
- Turbocharger Maintenance
- Regularly inspect the turbocharger for signs of wear or damage
- Ensure the turbocharger is clean and there is no carbon buildup (carbon buildup may require professional cleaning to remove)
- Timing Belt Replacement
- Replace the timing belt every 60,000 to 100,000, depending on recommendation from the manufacturer.
- To replace the timing belt:
- Remove the old belt
- Install the new belt, aligned with the timing marks
Symptom-Based Troubleshooting
Even with the most diligent and painstaking regular maintenance, diesel engines can still run into problems. Here are some common complaints, their possible causes, and ways to fix the problems:
Hard Starting
Causes: Faulty glow plugs; low compression; air in the fuel system.
Solutions:
- Replace faulty glow plugs
- Check fuel injection system for leaks
- Run a compression test
Power Loss
Causes: Clogged fuel or air filters; turbocharger issues; injector problems.
Solutions:
- Replace any clogged filters
- Inspect and clean the turbocharger
- Clean and/or replace faulty injectors
Overheating
Causes: Low coolant; radiator issues; faulty thermostat.
Solutions:
- Check and potentially top up coolant
- Inspect the radiator for leaks and/or blockages
- Replace the thermostat
Excessive Black or Gray Smoke
Causes: Faulty injectors; turbocharger issues; EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) valve problems
Note: The aftertreatment device could be a secondary failure. This device should always be checked for internal damage any time there is heavy exhaust smoke.
Solutions:
- Clean or replace faulty injectors
- Inspect and clean the turbocharger
- Check and clean the EGR valve
Not sure what’s causing the problem? Diesel Repair’s Symptom-Based Troubleshooting module can help! Symptom-Based Troubleshooting searches for step-by-step maintenance procedures based on Industry, Make, Model, Year, AND Symptom. Diesel Repair also offers in-depth Wiring Instructions, Testing Procedures, the ability to search by Fault Code, and more!
Seasonal Maintenance Tips
Weather changes can have a significant impact on the performance of a diesel engine. Here are a few key points to consider during warm and cold months to keep your engine running at its peak throughout the year.
Summer
High temperatures can stress a diesel engine’s cooling system. Regular maintenance of these parts can help prevent overheating.
- Cooling System – Ensure the cooling system is working properly.
- Air Conditioning – Check the air conditioning efficiency.
Winter
Cold temperatures can affect an engine’s starting ability and fuel efficiency. Proper winter maintenance helps prevent fuel gelling, ensures easy cold starts, and keeps the engine running smoothly.
- Fuel Additives – Using anti-gel additives can prevent diesel fuel from becoming too cold.
- Battery Check – Ensuring that the battery is fully charged and in good working condition aids in cold starts.
- Glow Plugs – Regularly checking glow plugs and replacing them as needed facilitates cold starts.
To find more maintenance tips and troubleshooting guides, visit Diesel Laptops’ Diesel Repair platform. Diesel Repair has everything you need to keep your truck running, whatever the next mile may bring. Best of all, Diesel Repair is available via mobile app or easy-to-use website. Free users can view quick repair info while paid subscribers get detailed, step-by-step service and repair instructions for every make and model in our always-expanding database.
